HOW DOES KETO DIET IMPACT ON LONG TIME HEALTH
Take a look at the effect of the high fat, low carbohydrate food regimen on the intestine microbiome, and the fitness implications of lengthy-time period ketogenic diets. First, a quick primer on the human intestine and
Take a look at the effect of the high fat, low carbohydrate food regimen on the intestine microbiome, and the fitness implications of lengthy-time period ketogenic diets.

First, a quick primer on the human intestine and microbiome. The term ‘intestine’ method the complete gastrointestinal tract, from mouth to anus. The belly harbors only a few microorganisms below regular situations, due to its intense acidity, and the upper small intestine is also adverse due to high concentrations of bile and different digestive juices. The huge intestine, but, is a extraordinary story. It presents really perfect surroundings for microorganisms: warm, moist, and complete of meals.
Our ‘microbial self’ thrives on a numerous array of carbohydrates – fibre, resistant starch and non-starch polysaccharides – found best in vegetation.
Whilst we communicate of ‘the intestine vegetation or microbiome’, we’re in most cases speak about the genetic cloth of the microorganisms that inhabit our massive intestine, or colon. The community of microorganisms themselves, about one hundred trillion of them, is known as ‘microbiota’ and its miles created from by and large micro-organism but also viruses, fungi and protozoa. Their collective genome is full-size (about 3 million genes versus 23000 genes in a person) and it’s far crucial to us because they produce hundreds of materials which can positively or negatively affect our fitness depending on what we feed them.
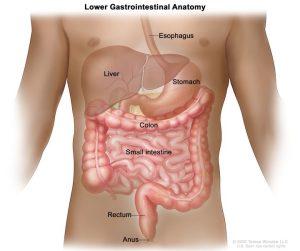
Whilst there’s no consensus at the ‘ideal’ composition of the human gut microbiota, there are particular patterns of dysbiosis – underrepresentation of certain bacterial species, and overrepresentation of others – which can be strongly related with a heightened chance of numerous sicknesses. Inflammatory bowel disease, weight problems, kind 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disorder, and cancer are just some of the diseases which have been connected to imbalanced gut microbiota.
Excessive fats Diets
A high-fats eating regimen has been found to reduce colon bacteria standard, at the same time as increasing general anaerobic microflora and Bacteroides counts. Bacteroides are generally useful organisms, however overgrowth is associated with inflammatory bowel ailment, intense, antibiotic-resistant infections, and colorectal cancer.
The ketogenic diet is characterised by way of being high in fats, very low in carbohydrates, and very low to moderately high in protein (relying on whether it is a classical or modified ketogenic diet.
A small examine of people affected by Glucose Transporter 1 Deficiency Syndrome (GLUT1 DS – a cause of epileptic seizures) located that after three months on a ketogenic eating regimen, there has been a huge growth in a group of bacteria acknowledged to supply hydrogen sulphide – a fuel which reasons gut infection and is connected to the development of inflammatory bowel disease.
In a look at of people at high hazard of metabolic syndrome, switching from a eating regimen excessive in saturated fat (typical of the ketogenic weight loss plan) to a low fats diet increased the numbers of beneficial Bifidobacterium, and this correlated with reduced fasting glucose and general ldl cholesterol – in different phrases, a reversal of metabolic syndrome.
A excessive fats diet will increase intestinal permeability – that is, it causes leaky gut, by using turning off the genes that code for proteins that include tight junctions, the ‘seals’ between neighbouring intestinal cells. Tight junctions are intended to prevent undesirable or dangerous intestine contents – which includes undigested proteins and bacterial pollutants – from leaking through the gut wall and into the bloodstream. One of these pollutants is endotoxin, a issue of the cellular walls of gram negative micro-organism. Saturated fats intake, specially, increases the absorption of endotoxin from the gut into the bloodstream and the ensuing endotoxemia triggers inflammation, and is associated with reduced glucose tolerance (which could in the end result in diabetes), weight benefit and oxidative pressure.
Humans stricken by predominant depressive disease had been determined to have better stages of serum antibodies in opposition to endotoxin than non-depressed human beings, indicating leaky gut and an immune reaction to endotoxemia might be associated with depression.
Excessive fat intake also increases the amount of bile secreted with the aid of the gallbladder into the small gut. This increases the relative abundance of bacterial species that use bile as a food supply. Excessive counts of those bacteria are associated with improved inflammation. High counts of Bilophila wadsworthia has been related to elevated incidence and severity of colitis and colorectal cancer, even as Alistipes become discovered to be overrepresented in humans laid low with foremost depressive disease.
Now not All Carbs Are Created same
Proponents of ketogenic diets tend to lump all carbohydrate-containing foods collectively, supplying them as the foundation motive of the persistent sicknesses that plague Westernized international locations.
But, when it comes to the intestine microbiome, all carbohydrates are not created same. Unrefined or minimally-processed carbohydrate-rich meals, consisting of whole grains, starchy veggies, legumes and culmination, include non-digestible carbohydrates which includes fibre, resistant starch and non-starch polysaccharides – dubbed ‘microbiota handy carbohydrates or MACs by using researchers.
In contrast to easy starches and sugars, these non-digestible carbohydrates aren’t broken down with the aid of human digestive enzymes inside the small intestine, and don’t serve as meals supply for us. As a substitute, they make it all of the way all the way down to the massive gut where our gut microbiota ferments them, producing not handiest a power source for themselves, however a host of compounds that are useful for their hosts – us.
A diet low in MACs reduces total bacterial abundance – one of the primary indicators of a healthy microbiota – and the richness of their microbiome. As leading intestine microbiome researchers, Erica and Justin Sonnenberg placed it, consuming a low carbohydrate eating regimen equates to “ravenous our microbial self “.
The effects of this impoverishment in general numbers and variety of gut bacteria aren’t but understood, but it’s worth noting that human beings who live a extra ‘primitive’ hunter gatherer way of life, such as the Hadza of northern Tanzania, have a long way extra microbial richness and biodiversity than common Westerners – a function linked to their excessive consumption of fibrous plant foods[21], and strongly correlated with their freedom from typical Western diseases consisting of weight problems, diabetes and colorectal most cancers.
One in all the products of bacterial fermentation of MACs – especially resistant starches and dietary fibre – is butyrate. Butyrate has an astonishingly various suite of benefits, which include:
- Providing the main gas supply to colonocytes (the cells lining the large gut)
- Keeping the integrity of the intestine lining (stopping and healing leaky intestine)
- Lowering mucosal inflammation
- Reducing visceral sensitivity
- Modulating intestinal motility
- Stopping and inhibiting colorectal cancer
- Decreasing serum cholesterol
- Lowering insulin resistance
- Supporting with weight reduction
- Preventing stroke
- Increasing brain derived neurotrophic component (BDNF), which stimulates the boom of latest nerve cells and connections among present ones.
Even ketogenic diets which can be excessive in fibre-rich however low-carbohydrate veggies can’t wish to acquire the quantity and diversity of MACs needed to domesticate a healthful and numerous gut microbiome. Non-fibre MACs which include resistant starch and non-starch polysaccharides are found maximum abundantly in entire grains, legumes and end result, now not greens.
The American gut venture – a large citizen technological know-how task that makes use of ‘massive facts’ to assist fill in knowledge gaps approximately the complex hyperlinks between our weight loss plan and lifestyle behaviour, gut microbiota, and fitness fame – these days pronounced that the unmarried best predictor of microbial diversity is the number of various plant meals eaten according to week. individuals who pronounced ingesting greater than 30 unique plant foods had the maximum diverse microbiota. It’s easy to consume this many distinct plant foods on a wholefood, plant-primarily based weight loss program, however really not possible on a ketogenic food plan that excludes most fruits, starchy veggies, whole grains and legumes.
Whole grain intake is continuously linked with progressed fitness – which include reduced chance of kind 2 diabetes, cardiovascular sickness, and weight benefit – and it’s far probable that a number of the blessings of entire grain consumption are mediated via their results on intestine microbes.
For example, diets wealthy in complete grain and wheat bran are linked to an boom inside the bacteria Bifidobacterial and Lactobacilli, whilst whole grain barley and resistant starches increase the abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria. Humans with superior colorectal cancer had been discovered to have a lower fibre consumption, decreased degrees of butyrate and other quick chain fatty acids, and lower counts of fibre-loving bacteria than most cancers-loose controls.
High Protein Diets
Whilst the classic ketogenic eating regimen includes much less protein than fat, a few versions are particularly heavy on protein – almost continuously animal proteins, because plant proteins come ‘packaged’ with carbohydrates.
Bile-tolerant anaerobes growth with consumption of animal-primarily based protein, while the beneficial micro-organism is depleted by excessive protein, low carbohydrate diets– and therefore, lower butyrate production is determined in humans following such diets.
Fewer butyrate-producing micro-organism are located inside the faeces of inflammatory bowel ailment sufferers than healthful manage sufferers. And, excessive animal protein consumption has been discovered to significantly growth the risk of growing this bowel ailment.
The dysbiotic pattern of accelerated Bacteroides and dwindled butyrate-generating micro-organism has also been recognized in colorectal cancer patients.
Summary
Excessive fats, low carbohydrate ketogenic diets reason principal disruptions to our microbiota, triggering leaky intestine and systemic irritation. Since the study of our microbiota remains in its infancy, the long-term effects of the dysbiosis triggered by means of ketogenic diets are unknown, but strong links are already obvious with some of chronic illnesses including inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal most cancers.
Our ‘microbial self’ flourishes on a numerous array of carbohydrates – fibre, resistant starch and non-starch polysaccharides – found simplest in flora. In case you want a healthy gut microbiome, and all the advantages that go with the flow from it, the solution is simple: devour greater plant life.



Williamclouh April 22, 2024
Полностью свежие события моды.
Исчерпывающие эвенты лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Приятное место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://ullafashion.ru/
[url=https://ullafashion.ru/]https://ullafashion.ru/[/url]
Randydeata April 26, 2024
Точно свежие новости модного мира.
Актуальные мероприятия известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Новое место для трендовых людей.
https://fashionessa.ru/
[url=https://fashionessa.ru/]https://fashionessa.ru/[/url]
VictorTob April 27, 2024
Наиболее стильные новости мира fashion.
Важные мероприятия всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, haute couture.
Свежее место для модных хайпбистов.
https://nbcollector.ru/
[url=https://nbcollector.ru/]https://nbcollector.ru/[/url]
KraigacegE May 7, 2024
Абсолютно свежие новости индустрии.
Актуальные мероприятия самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Свежее место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://metamoda.ru/
[url=https://metamoda.ru/]https://metamoda.ru/[/url]
HarryVex May 12, 2024
Полностью свежие новинки мировых подиумов.
Исчерпывающие эвенты самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Самое приятное место для стильныех людей.
https://femalemoda.ru/
PeterHerse May 14, 2024
Наиболее трендовые события моды.
Актуальные эвенты известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Самое приятное место для трендовых людей.
https://breakmoda.ru/
JeffreyClide May 23, 2024
Fashion, luxe, travel
First style home for hypebeasts and cute people.
Style news, events. Latest collections, collaborations, drops.
https://dubai.luxepodium.com/
Louisexpah May 23, 2024
[url=https://b-p.sale]купить инстаграм брут аккаунты родная почта[/url] – дешевые аккаунты vk, магазин аккаунтов инстаграм авторег
PodiumHM May 28, 2024
Абсолютно все трендовые новости мира часов – новые новинки лучших часовых марок.
Точно все коллекции часов от доступных до ультра дорогих.
https://podium24.ru/
TimothyRab May 28, 2024
Абсолютно стильные события подиума.
Исчерпывающие события известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Новое место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://furluxury.ru/
Louismor June 1, 2024
Наиболее стильные события моды.
Актуальные мероприятия известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Свежее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://balenciager.ru/
JerryDully June 9, 2024
Самые стильные события моды.
Актуальные новости известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://luxe-moda.ru/
DonaldZonry June 13, 2024
Абсолютно трендовые новости подиума.
Важные эвенты всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, гедонизм.
Приятное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://fashion5.ru/
BryanZELRY June 14, 2024
[url=https://kraker14at.com]kraken14.at[/url] – kraken шоп, kraken даркнет
슬롯 June 15, 2024
geinoutime.com
이때 Zhu Houzhao는 약간 웃으며 “아버지, 이건 틀렸어요”라고 말했습니다.
Zofiaboite June 18, 2024
Самые трендовые новинки индустрии.
Важные новости известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Интересное место для трендовых людей.
https://whitesneaker.ru/
DarrellSoica June 18, 2024
Полностью свежие новости подиума.
Все эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://rfsneakers.ru
JasonLow June 18, 2024
[url=https://mounjaro-medical.ru]mounjaro 2.5 купить[/url] – самый безопасный препарат +для похудения, моунжаро
sale June 19, 2024
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.online/]20 mg dexamethasone[/url]
Orvilledipsy June 20, 2024
Несомненно трендовые новости мировых подиумов.
Актуальные мероприятия лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Интересное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://modavmode.ru
RichardStono June 21, 2024
Абсолютно свежие новости индустрии.
Важные эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, гедонизм.
Лучшее место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://miramoda.ru
Davidamert June 22, 2024
Несомненно трендовые новости подиума.
Важные события лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://urban-moda.ru/
Pablonomma June 23, 2024
Абсолютно стильные новинки моды.
Исчерпывающие новости мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех людей.
https://sofiamoda.ru
Willietut June 25, 2024
Наиболее важные события моды.
Все новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Самое приятное место для стильныех людей.
https://fashionsecret.ru
Lewisdup June 25, 2024
visite site [url=https://keplrwallet.app]Dym wallet keplr[/url]
DebraTerlY June 26, 2024
Полностью важные новинки модного мира.
Актуальные события лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Интересное место для модных людей.
https://worldsfashion.ru/
PillsErymn June 26, 2024
Rybelsus – Quick and Easy Weight Lass
According to randomised controlled trials, you start losing weight immediately after taking Rybelsus. After one month, the average weight loss on Rybelsus is around 2kg; after two months, it’s over 3kg.
What does Rybelsus do to your body?
Rybelsus (oral semaglutide) is a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It mimics a fullness hormone called GLP-1.
Rybelsus reduces appetite and hunger by interacting with the brain’s appetite control centre, the hypothalamus. This effect on the brain helps you eat fewer calories and starts almost immediately after taking the pill.
However, you might notice your hunger levels rising and falling in the first 4-5 weeks you take Rybelsus.
It can take around 4-5 weeks for Rybelsus to reach a level in the body we call a steady state. A steady state is when the drug’s levels in the body remain consistent rather than spiking and falling.
Interestingly, this initial weight loss is no different to other weight loss treatments or the impact of diet interventions on weight loss. The real effect of oral semaglutide is seen beyond three months.
Oral semaglutide is a long-acting medication that’s started at a lower dose to reduce the number and severity of side effects as it’s built up to a higher maintenance dose.
https://true-pill.top/rybelsus.html
drug July 2, 2024
[url=http://avermox.com/]vermox us[/url]
najlepsze escape roomy July 5, 2024
Great article and right to the point. I don’t know if this is truly the best place to ask but do you folks have any thoughts on where to employ some
professional writers? Thanks in advance 🙂 Najlepsze escape roomy
Jake G July 6, 2024
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was searching for!!
Kissimmee July 21, 2024
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site. I really hope to see the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own site now 😉
asbestos removal near me July 22, 2024
I could not resist commenting. Well written!
Flum float July 22, 2024
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Best wishes! Where are your contact details though?
lehenga July 24, 2024
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this article! It is the little changes that will make the largest changes. Thanks for sharing!